External Sensor API
Send weather and environmental data from your own sensor station directly into the AllskyKamera network.
Overview
The Weather API allows you to attach external sensors such as weather stations, SQM meters or other devices to your camera. The measurements are stored in the central InfluxDB and can be used in Grafana, on the camera page or in your own analyses.
The API is intentionally simple: you send a timestamp, a name for your sensor station and a flexible fields object with your measurements.
Access & API Key
The API is only intended for cameras that are part of the AllskyKamera network. The API key is identical to the secret key of your camera and links the data to the correct camera.
Requirements
- You operate a camera that is part of the AllskyKamera network.
- You received a valid secret key for your camera.
- You use this secret key as API key in the HTTP header.
Endpoint & Authentication
Endpoint URL
POST https://allskykamera.space/api/v1/weather.php
GET https://allskykamera.space/api/v1/weather.php
HTTP method
GET, POST, HTTPS only
Authentication (header)
X-API-Key: <DEIN_GEHEIMER_KAMERA_KEY>
Content-Type
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
The API key is transmitted via HTTP header only and should never be exposed in public repositories or client code.
Request structure
The request is sent as a JSON body via POST. The structure is generic so you can send any numeric measurements you like.
Example request (JSON)
{
"timestamp": "2025-01-01T23:15:00Z",
"ext_sensor": "Test_Sensor",
"fields": {
"temp_c": 22.9,
"hum_pct": 48.5,
"pressure_hpa": 1002.8
}
}Fields in the request
timestamp– Timestamp in ISO8601 format in UTC (e.g. 2025-01-01T23:15:00Z).ext_sensor– Name of your sensor station (free text, e.g. “Roof station”, “School garden”).fields– Object containing the measurements as key/value pairs (numeric values only).
Typical field names are e.g. temp_c (°C), hum_pct (% relative humidity) or pressure_hpa (air pressure in hPa). You may also use your own names, for example with a sensor prefix like BME280_temp_c or DS18B20_temp_c, as long as they are technically valid.
Multiple sensors in one station
If your station consists of several sensors (e.g. BME280, DS18B20, TSL2591), you can include the sensor name in the field names. This keeps values clearly identifiable later – for example BME280_temp_c, BME280_hum_pct or DS18B20_temp_c.
Example with multiple sensors
{
"timestamp": "2025-01-01T23:20:00Z",
"ext_sensor": "Dachstation",
"fields": {
"BME280_temp_c": 22.9,
"BME280_hum_pct": 48.5,
"DS18B20_temp_c": 21.3
}
}GET: Read access
With GET you can query your camera data from Influx. Authentication is done via your camera API key. The API automatically restricts results to your own camera (tag "kamera").
Endpoint
GET https://allskykamera.space/api/v1/weather.php
Authentication header
X-API-Key: <DEIN_GEHEIMER_KAMERA_KEY>
Query parameters
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
measurement |
string |
ext_sensors |
Influx measurement name (e.g. "ext_sensors", "SQM", "raspistatus"). |
fields |
string |
(optional) |
Comma-separated list of fields to return (e.g. "temp_c,hum_pct"). If omitted, all fields may be returned depending on the measurement. |
hours |
int |
24 |
Time range in hours (used if "start" is not set). |
start |
string |
(optional) |
Alternative time range (e.g. "-6h", "-7d"). Overrides "hours" if set. |
limit |
int |
500 |
Maximum number of rows returned. |
pivot |
0|1 |
0 |
If 1: returns pivoted (wide) format: one row per time with columns per field. |
aggregate |
none|mean|last|min|max |
none |
Optional aggregation function. |
every |
duration |
0 |
Aggregation interval (e.g. "1m", "5m"). Use "0" to disable aggregation. |
ext_sensor |
string |
(optional) |
Optional filter for tag "ext_sensor" (mainly for measurement "ext_sensors"). |
Note: The API key determines your camera ID. It is not possible to query other cameras.
Response formats
Long format (default)
[
{
"time": "2026-01-30T11:20:00Z",
"value": 18.42,
"field": "raspiDiskFree",
"measurement": "raspistatus",
"kamera": "ASK999"
}
]Pivot / wide format (pivot=1)
[
{
"time": "2026-01-30T11:20:00Z",
"raspiDiskFree": 18.42,
"kamera": "ASK999",
"host": "host1"
}
]Response & error codes
Successful response (example)
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{
"status": "ok"
}Error response (example)
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Content-Type: application/json
{
"error": "Missing fields (timestamp, fields)"
}400– Invalid request (e.g. missing fields like timestamp or fields).401– Missing or invalid API key.405– Wrong HTTP method (only POST is supported).429– Too Many Requests (rate limit exceeded)500– Internal server error.
Limits & usage quotas
To keep the infrastructure stable, each camera has certain daily and monthly limits for API calls. These limits apply automatically to all cameras in the network.
PUT / data upload limits
- Daily: 5,000 PUT requests (default: 3 values × 1,440 minutes = 4,320).
- Monthly: 130,000 PUT requests (approx. 30 days × 4,320 = 129,600).
GET / data retrieval limits
- Daily: 600 GET requests.
- Monthly: 6,000 GET requests.
Limits apply per camera. If you need higher measurement frequencies permanently, please contact the administration.
Examples
Make sure to use physically meaningful units (e.g. °C, hPa, % RH). The exact interpretation happens later during analysis.
Python example using requests
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import requests
from datetime import datetime, timezone
API_URL = "https://allskykamera.space/api/v1/weather.php"
API_KEY = "DEIN_GEHEIMER_KAMERA_KEY"
def main():
timestamp = datetime.now(timezone.utc).strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ")
payload = {
"timestamp": timestamp,
"ext_sensor": "Test_Sensor",
"fields": {
"temp_c": 22.9,
"hum_pct": 48.5,
"pressure_hpa": 1002.8
}
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-API-Key": API_KEY,
}
resp = requests.post(API_URL, headers=headers, json=payload, timeout=10)
print(resp.status_code, resp.text)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Python (GET / read)
import requests
API_URL = "https://allskykamera.space/api/v1/weather.php"
API_KEY = "DEIN_GEHEIMER_KAMERA_KEY"
params = {
"measurement": "raspistatus",
"fields": "raspiDiskFree",
"hours": 24,
"aggregate": "mean",
"every": "5m",
"pivot": 1,
"limit": 1000
}
r = requests.get(API_URL, params=params, headers={"X-API-Key": API_KEY}, timeout=10)
print(r.status_code)
print(r.json()[:3])Example using curl
curl -X POST "https://allskykamera.space/api/v1/weather.php" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "X-API-Key: DEIN_GEHEIMER_KAMERA_KEY" \
-d '{
"timestamp": "2025-01-01T23:15:00Z",
"ext_sensor": "Test_Sensor",
"fields": {
"temp_c": 22.9,
"hum_pct": 48.5,
"pressure_hpa": 1002.8
}
}'curl (GET / read)
curl -X GET "https://allskykamera.space/api/v1/weather.php?measurement=raspistatus&fields=raspiDiskFree&hours=24&aggregate=mean&every=5m&pivot=1&limit=1000" \
-H "X-API-Key: DEIN_GEHEIMER_KAMERA_KEY"ESP32 / Arduino example
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <HTTPClient.h>
const char* ssid = "DEIN_WLAN";
const char* password = "DEIN_PASSWORT";
const char* apiUrl = "https://allskykamera.space/api/v1/weather.php";
const char* apiKey = "DEIN_GEHEIMER_KAMERA_KEY";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("WLAN verbunden");
}
void loop() {
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) {
HTTPClient http;
http.begin(apiUrl);
http.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
http.addHeader("X-API-Key", apiKey);
String payload = R"({
"timestamp": "2025-01-01T23:15:00Z",
"ext_sensor": "ESP32_Weather",
"fields": {
"temp_c": 23.4,
"hum_pct": 51.2
}
})";
int httpCode = http.POST(payload);
String response = http.getString();
Serial.printf("HTTP: %d\n", httpCode);
Serial.println(response);
http.end();
}
delay(60000); // alle 60 Sekunden
}Usage on the camera page
Values sent via the API are first stored in InfluxDB only. In your user area you decide which sensors are shown on your camera page, how they are named and in which groups they appear.
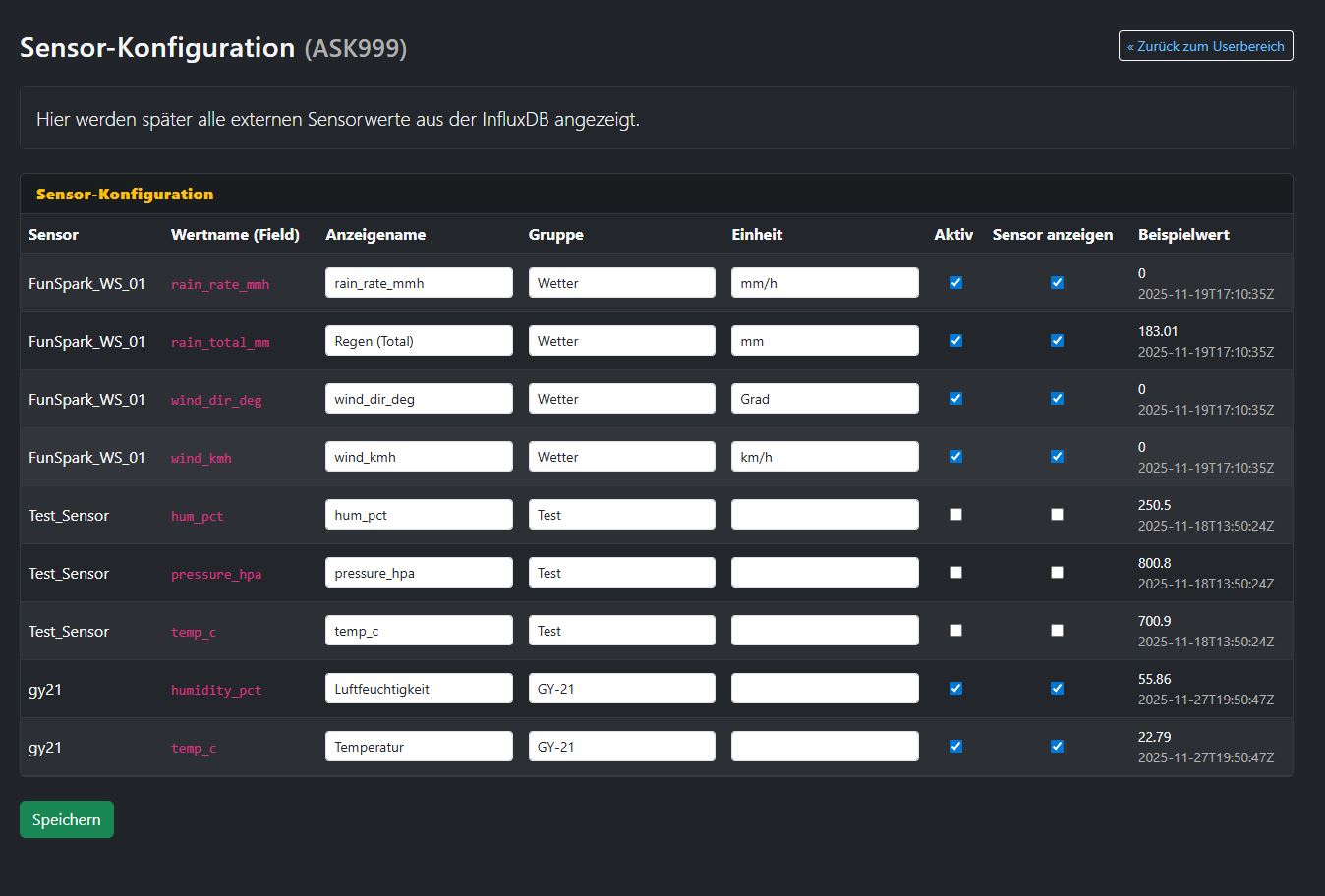
- Log in to your user area and open the tile “External sensors”. There you will find a button labelled “Open sensor configuration”.
- In the sensor configuration you see all fields that your station has sent via the API. For each field you can set a display name, a group and a unit and choose whether the sensor is active and visible on the website.
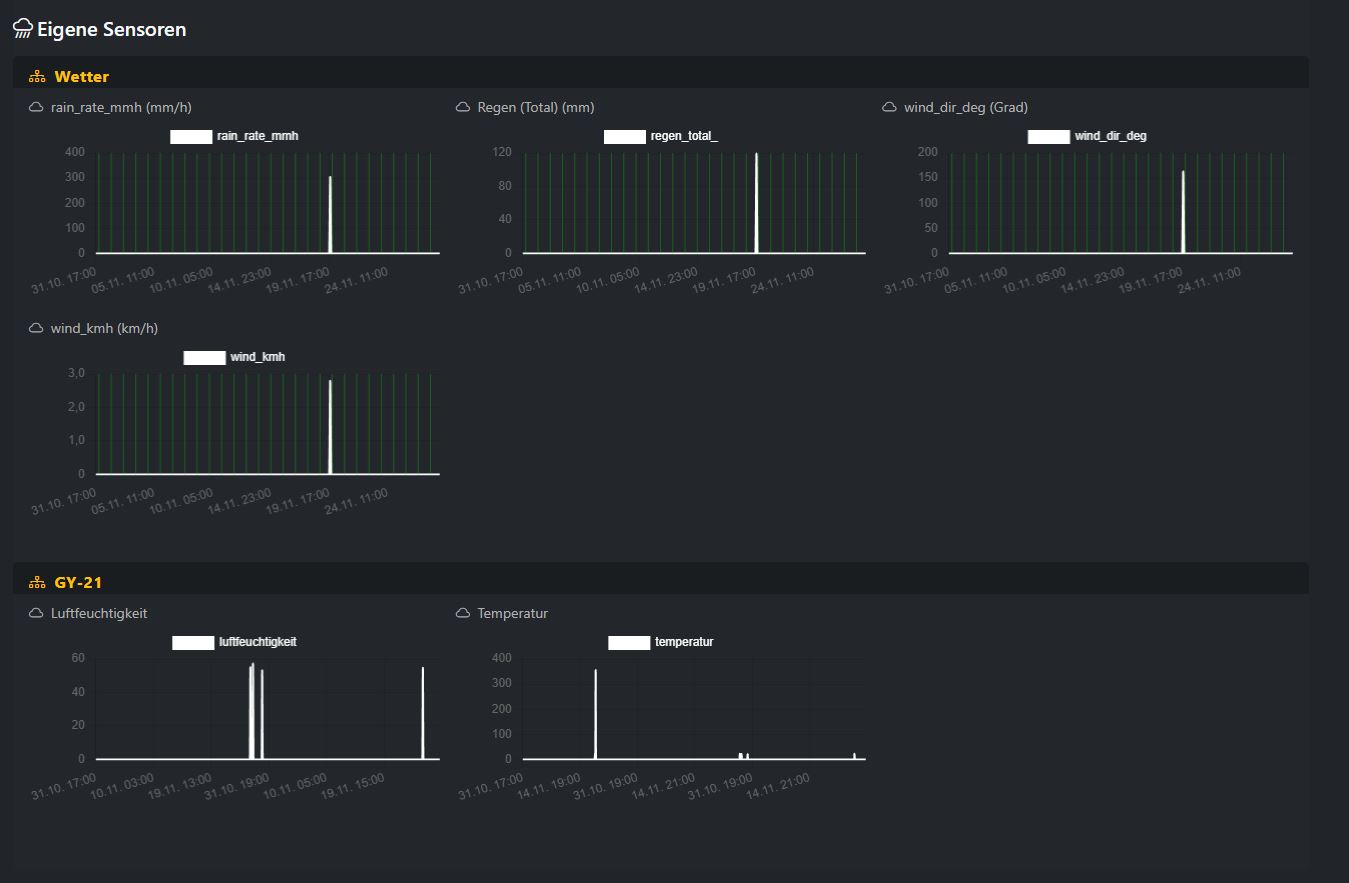
- After saving, a section “Own sensors” appears on your camera page. The charts are grouped (e.g. “Weather”, “GY-21”). Only sensors with the “show sensor” flag enabled are rendered.
Tip: Use meaningful groups and clear display names (e.g. “Weather”, “GY-21”, “Indoor”) so visitors can understand your measurements at a glance.